Optimizing Tax Planning Based On Residential Status: Unlock Your Financial Potential Today!
Tax Planning Based on Residential Status
Introduction
Dear Readers,
3 Picture Gallery: Optimizing Tax Planning Based On Residential Status: Unlock Your Financial Potential Today!
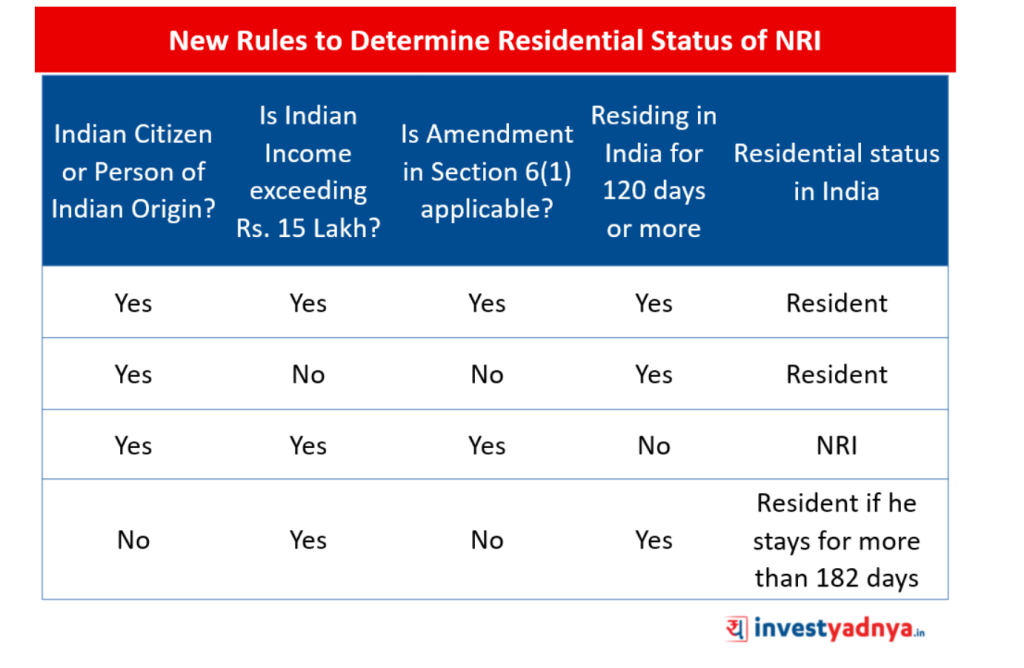
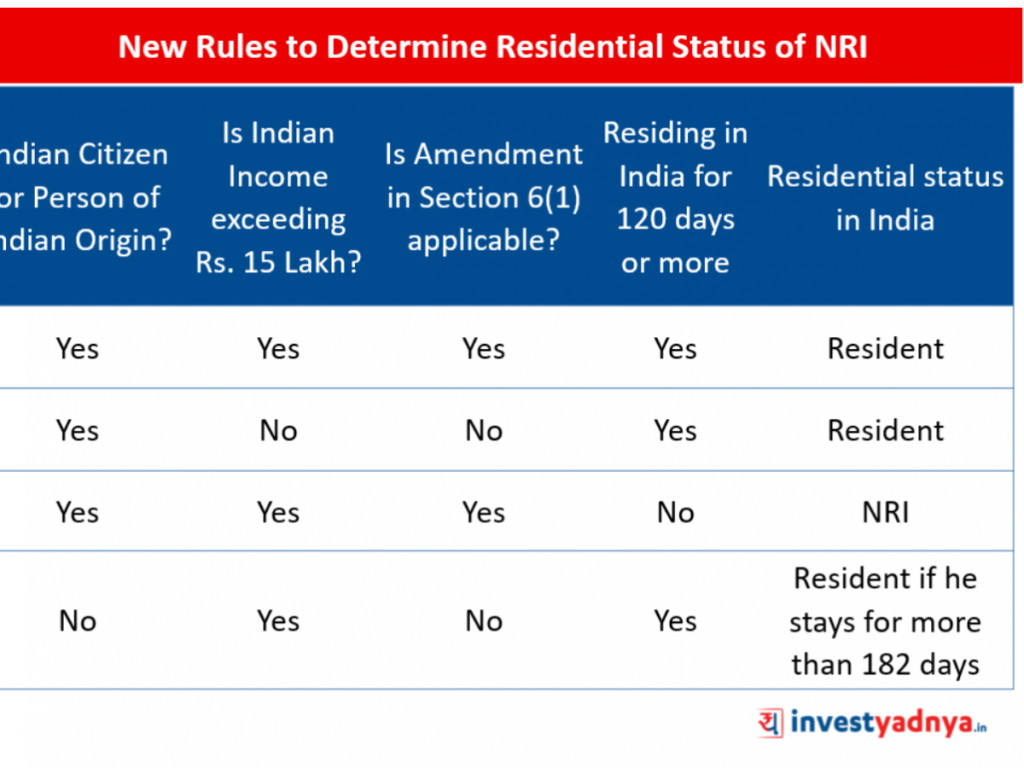
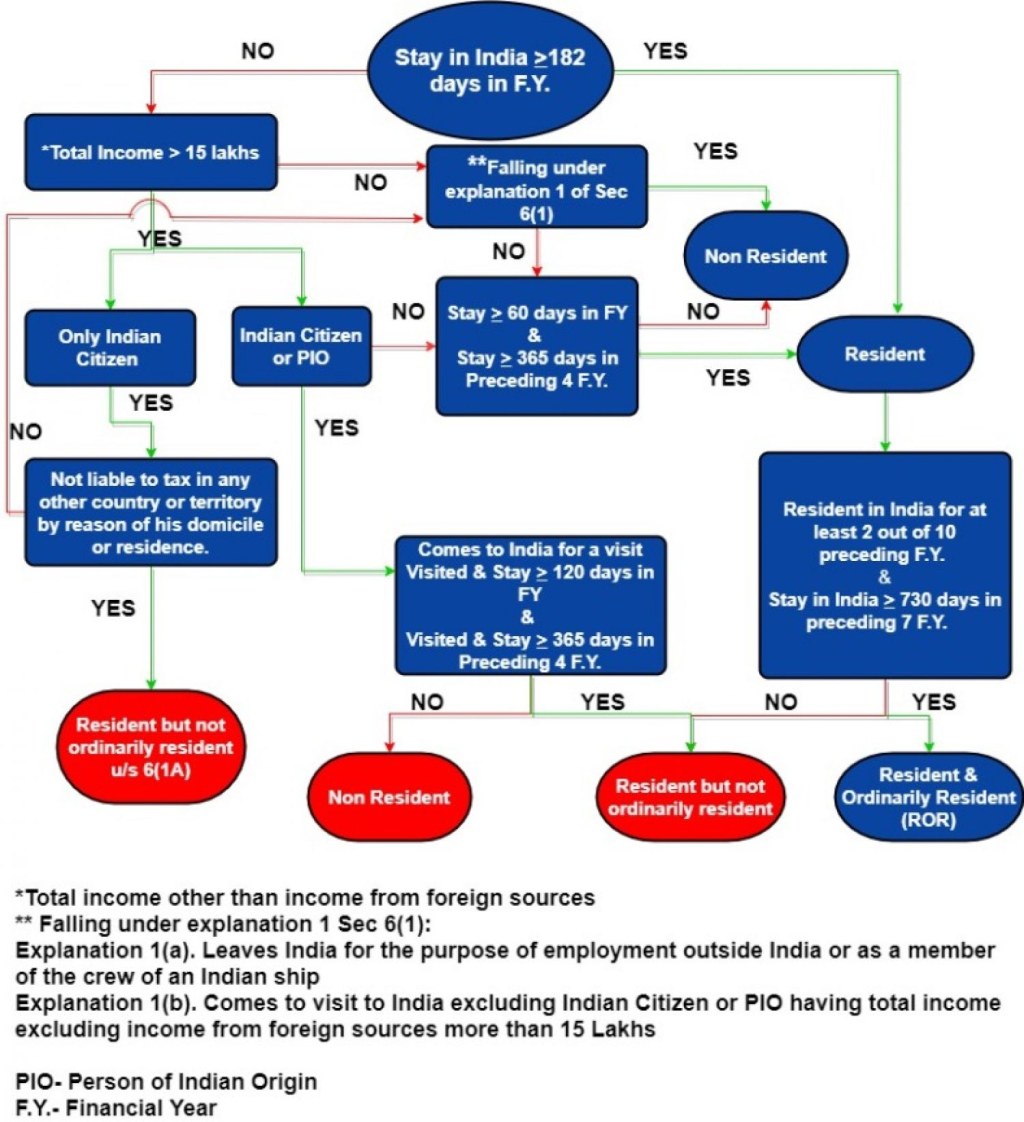
Welcome to our article on tax planning based on residential status. In today’s globalized world, individuals and businesses have the opportunity to live and work in different countries, often resulting in complex tax implications. Understanding and efficiently managing these tax implications can lead to significant financial benefits.

Image Source: investyadnya.in
In this article, we will explore the concept of tax planning based on residential status, providing you with valuable insights and strategies that can help optimize your tax position. Whether you are an individual seeking to minimize your tax liability or a business navigating cross-border taxation, this article aims to equip you with the necessary knowledge to make informed decisions.
So, let’s dive deeper into the world of tax planning based on residential status and discover how it can work to your advantage.
What is Tax Planning Based on Residential Status?
🔍 Tax planning based on residential status refers to the strategic management of one’s tax obligations and liabilities by considering the individual or business’s residency status for tax purposes. Residency status plays a crucial role in determining the tax jurisdiction that has the right to tax an individual’s income or a business’s profits.

Image Source: investyadnya.in
🔍 It is important to note that tax planning based on residential status is a legal and ethical practice aimed at optimizing tax efficiency within the boundaries of tax laws and regulations. It involves analyzing the tax implications of different residency statuses and utilizing available legal strategies to minimize tax liabilities.
🔍 The concept of tax planning based on residential status is particularly relevant in cases where individuals or businesses have connections to multiple countries, such as dual citizenship, residency in different jurisdictions, or international business operations.

Image Source: carajput.com
🔍 By understanding the tax laws and regulations of different countries and strategically managing residency status, individuals and businesses can potentially reduce their overall tax burden, avoid double taxation, and take advantage of tax incentives and benefits provided by specific jurisdictions.
🔍 Now that we have a basic understanding of tax planning based on residential status, let us delve into the specifics of who can benefit from it and when it becomes relevant.
Who Can Benefit from Tax Planning Based on Residential Status?
🔍 Individuals: Individuals who have multiple citizenships or residence permits, frequently travel or reside in different countries, or work internationally can benefit from tax planning based on residential status. By strategically managing their residency status, they can potentially reduce their tax liabilities and take advantage of tax incentives in specific jurisdictions.
🔍 Expatriates: Expatriates, individuals temporarily residing in a foreign country for work purposes, often have complex tax situations. Tax planning based on residential status can help them optimize their tax position by considering factors such as tax treaties, tax exemptions, and eligibility for foreign tax credits.
🔍 Digital Nomads: With the rise of remote work and digital entrepreneurship, individuals who work online and travel frequently fall into the category of digital nomads. Tax planning based on residential status can help them navigate the tax implications of their nomadic lifestyle and potentially reduce their tax liabilities.
🔍 Businesses: Businesses with international operations, subsidiaries, or branches may benefit from tax planning based on residential status. By strategically managing their corporate residency status and considering factors such as transfer pricing, tax treaties, and tax incentives, businesses can optimize their global tax position.
🔍 It is important to consult with tax professionals or experts specializing in international taxation to ensure compliance with relevant tax laws and regulations while implementing tax planning strategies based on residential status.
When Does Tax Planning Based on Residential Status Become Relevant?
🔍 Tax planning based on residential status becomes relevant in various scenarios, such as:
🔸 Relocating to a new country: When an individual or business decides to relocate to a new country, it is crucial to assess and plan for the tax implications of the new residency status. This includes understanding the tax laws and regulations of the destination country, potential tax incentives, and any tax treaty agreements between countries.
🔸 Dual residency or citizenship: Individuals with dual residency or citizenship in different countries may face complex tax situations. Tax planning based on residential status can help them determine their primary residency for tax purposes and strategically manage their tax obligations.
🔸 International business expansion: When businesses expand their operations to foreign countries, tax planning based on residential status becomes crucial. It involves analyzing the tax implications of different jurisdictions, considering transfer pricing regulations, and structuring the business in a tax-efficient manner.
🔸 Cross-border investments: Individuals or businesses investing in assets or ventures across borders need to consider the tax consequences. Tax planning based on residential status can help optimize the tax position by considering factors such as withholding taxes, capital gains taxes, and tax treaties.
🔸 Exiting a country: When individuals or businesses cease their residency or operations in a country, proper tax planning based on residential status is essential. This includes understanding exit tax provisions, potential tax liabilities upon exit, and ensuring compliance with reporting requirements.
🔍 In all of these scenarios, tax planning based on residential status can provide individuals and businesses with valuable strategies to minimize tax liabilities, avoid double taxation, and maximize tax benefits.
Where Can Tax Planning Based on Residential Status Be Applied?
🔍 Tax planning based on residential status can be applied globally, as it considers the tax implications of different countries and jurisdictions. It is especially relevant in countries with complex tax systems, high tax rates, or those offering tax incentives and benefits to attract individuals and businesses.
🔍 Some popular destinations for tax planning based on residential status include countries with territorial taxation systems, low or no personal income taxes, and favorable tax regimes for businesses. Examples include Singapore, Hong Kong, Switzerland, the United Arab Emirates, and various offshore jurisdictions.
🔍 However, it is essential to note that tax planning based on residential status should be approached with caution and within the boundaries of tax laws and regulations of the countries involved. Seeking professional advice from tax experts with expertise in international taxation is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
Why is Tax Planning Based on Residential Status Important?
🔍 Tax planning based on residential status is important for several reasons:
🔸 Tax optimization: By strategically managing residency status, individuals and businesses can potentially reduce their overall tax burden and optimize their tax position.
🔸 Avoiding double taxation: Understanding the tax laws and regulations of different countries and leveraging tax treaties can help individuals and businesses avoid being taxed on the same income or profits in multiple jurisdictions.
🔸 Maximizing tax incentives and benefits: Tax planning based on residential status allows individuals and businesses to take advantage of tax incentives and benefits offered by specific jurisdictions, such as tax exemptions, deductions, or reduced tax rates.
🔸 Compliance with tax laws: Proper tax planning based on residential status ensures compliance with tax laws and regulations of the relevant jurisdictions, minimizing the risk of penalties, audits, or legal issues.
🔸 Long-term financial planning: Tax planning based on residential status plays a crucial role in long-term financial planning, allowing individuals and businesses to allocate resources efficiently and make informed decisions regarding investments, retirement, and estate planning.
🔍 Given these benefits, tax planning based on residential status is a valuable tool for individuals and businesses looking to optimize their tax position and achieve financial goals.
How Does Tax Planning Based on Residential Status Work?
🔍 Tax planning based on residential status involves a systematic approach to assess an individual or business’s residency status for tax purposes, analyze the tax implications, and implement strategies to optimize the tax position. Here’s how it works:
1️⃣ Assess residency status: Determine the individual or business’s residency status based on the relevant tax laws and regulations. This includes considering factors such as physical presence, permanent establishment, or the number of days spent in a country.
2️⃣ Analyze tax implications: Understand the tax laws and regulations of the countries involved and analyze the tax implications of different residency statuses. Consider factors such as tax rates, tax exemptions, tax treaties, and available tax incentives.
3️⃣ Evaluate tax treaties: If applicable, assess the tax treaty agreements between countries to determine the tax jurisdiction that has the right to tax specific types of income or profits. Understand the provisions related to residency tie-breaker rules, which determine the primary residency for tax purposes in cases of dual residency.
4️⃣ Strategically manage residency status: Based on the analysis of tax implications and tax treaties, strategically manage residency status to optimize the tax position. This may involve relocating to a jurisdiction with favorable tax conditions, establishing residency in a tax-efficient manner, or structuring business operations to minimize tax liabilities.
5️⃣ Implement tax planning strategies: Implement tax planning strategies based on the assessed residency status. These strategies may include utilizing tax-efficient investment vehicles, leveraging tax incentives, utilizing foreign tax credits, or restructuring business operations.
6️⃣ Ongoing monitoring and compliance: Regularly monitor tax laws and regulations of the relevant jurisdictions to ensure ongoing compliance and adapt tax planning strategies as needed. Stay informed about changes in tax laws, reporting requirements, and any updates to tax treaties that may impact the residency status and tax obligations.
🔍 By following this systematic approach, individuals and businesses can effectively utilize tax planning based on residential status to optimize their tax position and achieve financial objectives.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tax Planning Based on Residential Status
Advantages:
1. 🌟 Reduced tax liabilities: By strategically managing residency status, individuals and businesses can potentially reduce their overall tax burden and keep more of their income or profits.
2. 🌟 Avoidance of double taxation: Tax planning based on residential status helps individuals and businesses avoid being taxed on the same income or profits in multiple jurisdictions, minimizing the risk of double taxation.
3. 🌟 Access to tax incentives: Certain jurisdictions offer tax incentives and benefits to attract individuals and businesses. By leveraging tax planning based on residential status, individuals and businesses can take advantage of these incentives, such as tax exemptions, deductions, or reduced tax rates.
4. 🌟 Flexibility and mobility: Effective tax planning based on residential status provides individuals and businesses with flexibility and mobility to live, work, and invest in different countries while optimizing their tax position.
5. 🌟 Long-term financial planning: By minimizing tax liabilities and optimizing tax position, tax planning based on residential status contributes to long-term financial planning, allowing individuals and businesses to allocate resources efficiently and achieve their financial goals.
Disadvantages:
1. 💔 Complexities and compliance: Tax planning based on residential status involves navigating complex tax laws and regulations of different countries. Ensuring compliance with relevant tax laws, reporting requirements, and avoiding potential legal issues can be challenging.
2. 💔 Need for professional advice: Due to the complexities involved, individuals and businesses engaging in tax planning based on residential status should seek professional advice from tax experts specializing in international taxation to ensure compliance and avoid potential pitfalls.
3. 💔 Changing tax laws and treaties: Tax laws and treaties can change over time, impacting the effectiveness of tax planning strategies based on residential status. Ongoing monitoring and adaptation of strategies are necessary to ensure continued compliance and optimization.
4. 💔 Potential reputational risks: Some jurisdictions offering tax incentives and benefits may be subject to scrutiny or criticism regarding their tax practices. Engaging in tax planning based on residential status should consider potential reputational risks and ethical considerations.
5. 💔 Administrative burdens: Tax planning based on residential status may involve additional administrative burdens, such as maintaining proper documentation, filing tax returns in different jurisdictions, and complying with reporting requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is tax planning based on residential status legal?
Yes, tax planning based on residential status is legal. It involves analyzing the tax implications of different residency statuses and utilizing available legal strategies to minimize tax liabilities within the boundaries of tax laws and regulations.
2. Are there risks involved in tax planning based on residential status?
Engaging in tax planning based on residential status may involve complexities, changing tax laws, and potential reputational risks. It is crucial to seek professional advice and ensure compliance with relevant tax laws to mitigate these risks.
3. Can tax planning based on residential status help minimize tax liabilities?
Yes, tax planning based on residential status can help minimize tax liabilities by strategically managing residency status, taking advantage of available tax incentives, and avoiding double taxation.
4. Do individuals and businesses need professional advice for tax planning based on residential status?
Yes, due to the complexities involved, individuals and businesses should seek professional advice from tax experts specializing in international taxation to ensure compliance with relevant tax laws and regulations.
5. Can tax planning based on residential status be applied to individuals only?
No, tax planning based on residential status can be applied to both individuals and businesses. It is particularly relevant for businesses with international operations or those considering expanding into foreign markets.
Conclusion
Dear Readers,
Throughout this article, we have explored the concept of tax planning based on residential status and its significance in optimizing tax positions for individuals and businesses. By strategically managing residency status, individuals and businesses can potentially reduce tax liabilities, avoid double taxation, and access tax incentives offered by specific jurisdictions.
However, it is essential to approach tax planning based on residential status with caution, ensuring compliance with relevant tax laws and seeking professional advice from tax experts specializing in
This post topic: Tax Planning
![Free Tax Estimate Excel Spreadsheet for // [Download]](https://allcredit.info/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/free-tax-estimate-excel-spreadsheet-for-download-150x150.jpg)

