Master Tax Planning 101: Maximize Profits With Smart Buy, Borrow, Die Strategies!
Tax Planning 101: Buy, Borrow, Die
Introduction
Dear Readers,
1 Picture Gallery: Master Tax Planning 101: Maximize Profits With Smart Buy, Borrow, Die Strategies!
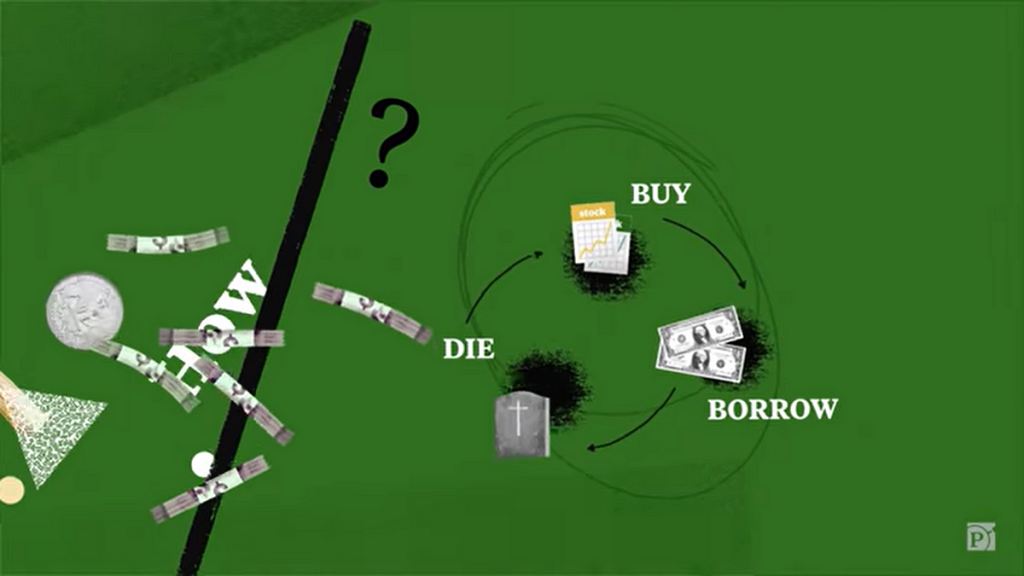
Today, we are going to discuss an essential aspect of financial planning – tax planning. Specifically, we will delve into a strategy known as Buy, Borrow, Die that can help individuals optimize their tax liabilities and maximize their financial well-being. In this article, we will explore what this strategy entails, who can benefit from it, when and where it should be implemented, why it is advantageous, and how to effectively execute it. So let’s dive in and discover how you can make the most of tax planning using the Buy, Borrow, Die approach.
Before we begin, let’s take a moment to understand the basic concept of tax planning. Tax planning involves employing various strategies to minimize the amount of tax payable by individuals and businesses. It is a legal and legitimate approach to manage your financial affairs and reduce the burden of taxation. By implementing effective tax planning strategies, you can potentially redirect your savings towards more productive investments, secure your financial future, and achieve your long-term goals.

Image Source: medium.com
Now, let’s explore the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy in detail, its benefits, drawbacks, and answers to frequently asked questions.
What is Tax Planning 101: Buy, Borrow, Die?
The Buy, Borrow, Die strategy is a tax planning technique that revolves around three key actions – buying assets, borrowing against them, and preserving their value until death. This approach aims to optimize the tax consequences of transferring assets to future generations while potentially minimizing the associated tax liabilities. Let’s break down each step:
1. Buying Assets
As part of this strategy, individuals purchase appreciating assets such as real estate, stocks, or businesses. The objective is to acquire assets that have the potential to increase in value over time.
2. Borrowing Against Assets
Once the assets are acquired, individuals can borrow against their value, using them as collateral. By doing so, they can access funds without triggering immediate tax consequences.
3. Preserving Value Until Death
Instead of selling the assets during their lifetime, individuals hold onto them until death. This approach allows for the potential elimination of capital gains tax, as the assets receive a step-up in basis upon inheritance.
By following these steps, individuals can potentially pass on their appreciated assets to their heirs, who can then sell them without incurring significant tax liabilities.
Who Can Benefit from Tax Planning 101: Buy, Borrow, Die?
The Buy, Borrow, Die strategy can be particularly advantageous for individuals with substantial assets and a desire to preserve their wealth for future generations. High-net-worth individuals, estate owners, and business owners looking to minimize estate taxes and maximize the value of their assets can benefit from this approach. It offers an opportunity to transfer wealth while potentially reducing the tax burdens associated with intergenerational asset transfers.
When and Where Should Tax Planning 101: Buy, Borrow, Die be Implemented?
The Buy, Borrow, Die strategy should be implemented after carefully considering various factors, including your financial goals, age, health, and estate planning objectives. It is crucial to consult with experienced tax professionals, financial advisors, and legal experts to ensure proper implementation. The strategy may vary depending on the jurisdiction’s tax laws, so it is essential to seek advice tailored to your specific circumstances.
Why Should You Consider Tax Planning 101: Buy, Borrow, Die?
There are several compelling reasons to consider the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy:
1. Tax Efficiency
By employing this strategy, individuals can potentially minimize their tax liabilities, allowing them to retain a larger portion of their wealth and pass it on to future generations.
2. Wealth Preservation
The Buy, Borrow, Die approach enables individuals to preserve their wealth and ensure that their assets are transferred to their heirs with minimal tax consequences.
3. Capital Gains Tax Elimination
By holding onto assets until death, individuals can potentially eliminate or reduce capital gains tax, as the assets receive a step-up in basis upon inheritance.
4. Estate Tax Reduction
This strategy offers an opportunity to reduce estate taxes, allowing individuals to pass on a greater portion of their assets to their intended beneficiaries.
5. Multi-Generational Planning
Implementing the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy can facilitate effective multi-generational planning, ensuring the smooth transfer of assets across generations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tax Planning 101: Buy, Borrow, Die
Advantages
1. Potential Tax Savings
By utilizing this strategy, individuals can potentially save significant amounts of money by minimizing their tax liabilities.
2. Wealth Preservation
The Buy, Borrow, Die approach allows individuals to preserve their wealth and ensure its transfer to future generations.
3. Increased Financial Flexibility
Borrowing against assets provides individuals with access to funds without triggering immediate tax consequences, allowing for increased financial flexibility.
Disadvantages
1. Complex Planning
Implementing the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy requires careful planning and coordination with tax and financial professionals due to its intricacies.
2. Market Volatility
The value of the assets purchased may fluctuate over time, exposing individuals to market risks.
3. Uncertain Future Tax Laws
Tax laws are subject to change, and future tax implications may impact the effectiveness of the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy legal?
Yes, the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy is a legal tax planning technique. However, it is crucial to comply with applicable tax laws and consult with professionals to ensure proper implementation.
2. Can anyone implement the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy?
The Buy, Borrow, Die strategy is most relevant for individuals with substantial assets and a desire to transfer wealth to future generations while minimizing tax liabilities. It may not be suitable for everyone, and individual circumstances should be evaluated before implementation.
3. What happens if tax laws change in the future?
Future changes in tax laws may impact the effectiveness of the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy. It is crucial to stay informed about tax law updates and consult with professionals to adjust your tax planning accordingly.
4. Are there any risks associated with the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy?
While the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy offers potential benefits, it also comes with certain risks, such as market volatility and uncertainty surrounding future tax laws. Consulting with professionals can help mitigate these risks.
5. How can I get started with tax planning using the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy?
To get started with tax planning using the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy, it is essential to consult with experienced tax professionals, financial advisors, and legal experts. They can help assess your financial situation, determine the suitability of this strategy, and guide you through its implementation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tax planning is a crucial aspect of financial management, and the Buy, Borrow, Die strategy offers a potential avenue to optimize tax liabilities and preserve wealth for future generations. By strategically buying assets, borrowing against them, and preserving their value until death, individuals can potentially minimize tax burdens while securing their financial legacies. However, it is important to seek professional advice and stay informed about tax laws to ensure effective implementation. So start exploring tax planning options today and secure your financial future.
Final Remarks
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial or legal advice. Please consult with qualified professionals before making any financial decisions or implementing tax planning strategies. The authors and publishers are not responsible for any actions taken based on the information provided.
This post topic: Tax Planning


